Whether you are a first time PC builder or are looking to gift your loved ones either a new computer or computer hardware to upgrade their build, it is important to carefully select components which gives you the best bang for your money.
A processor is an extremely important component of a computer, and it is of absolute importance that you buy the one which serves you the best. It can be daunting once you do start looking for processors as there is a huge variety of options to choose from, with names seemingly named by kids by smashing their keyboard. If you too are confused about what all these numbers and alphabets in these names means don’t worry you have come to the right place.
In this article, we will try to explain what all the numbers and alphabets used in the names of processors by Intel mean. This will help you better understand the difference between different processors from the company and allow you to make a more informed choice.
Intel makes use of a structure which is as follows:
- The processor’s intended target audience/Tier.
- Generation of the Chip.
- Performance Number/Model Number.
- An Alphabet denoting additional important information about the processor. (this is optional)
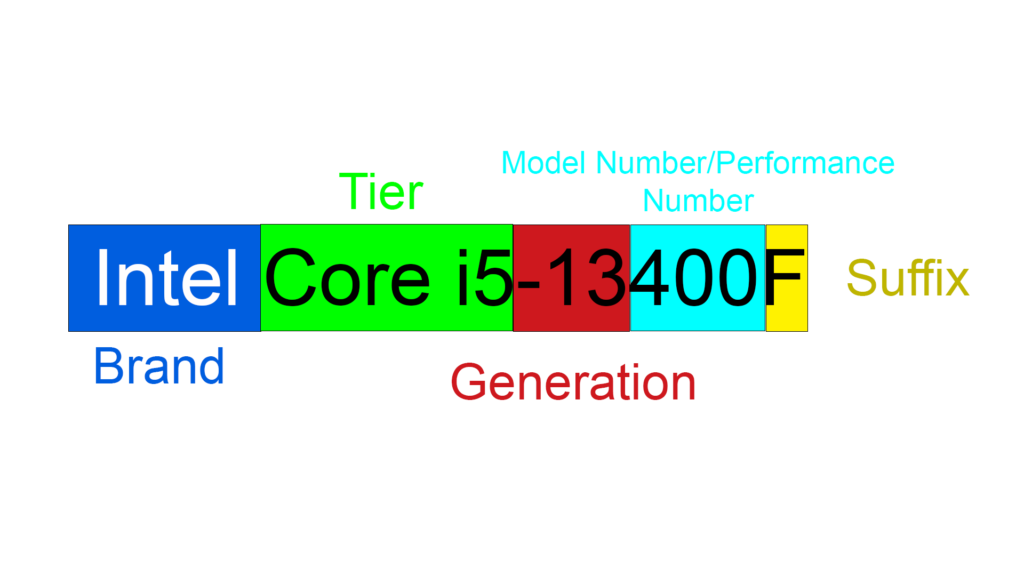
Intel follows a very easy to understand and streamlined naming conventions, which is great as it is easy to understand, and once you learn it, it becomes very easy to compare different offerings from the company with each other and the competition. Here is the kicker, Intel is soon going to adopt a new convention, but don’t worry we will cover that too in this article.
Let’s begin at the basics, you surely must have heard about Core i3, i5 or i9, but what do they really mean?
Core i3, i5, i7 and i9 are brand specific names used by Intel to give a general indication towards the performance and the price of the processor.
A Core i3 processor will be generally, cheaper, and less powerful than a Core i5 processor. So, on and so forth. However, this is not always the case due to different generations of a processor as we will see shortly.
Core i3: Core i3 processors are Intel’s most basic options, these are less powerful and are cheaper and therefore are targeted at people who don’t do a lot of multitasking and gaming. They are perfect for people who are looking to just browse the web and use Office application such as Word or PowerPoint.
Core i5: These processors are Intel’s offering for most everyday user, as they are great for multitasking and moderate gaming. They are however expensive from Core i3 processors, but they make it up for that extra cost by their performance.
Core i7: These processors are targeted towards, content creators and gaming enthusiasts, and therefore are much more powerful than Core i5 processors but cost more. When paired with the right GPU, a core i7 processor is more than enough to meet all your needs, be it either AAA gaming or video editing.
Core i9: These are Intel’s flagship processors, and thus are the most powerful and expensive processors (from intel) on which you can get your hands on. They boast, high core counts and clock speeds and generally require better cooling such as liquid coolers to keep their temps in line.
NOTE: Desktop processors always perform better than their laptop/mobile variants due to a lack of adequate cooling solution. Therefore, you might see a desktop Core i7 processor beating a Core i9 mobile processor.
AMD too have their own brand specific name (don’t worry we have a separate article for team red!) Ryzen 3, 5, 7 and 9 with similar meaning to that of Core I names. Therefore, Intel and AMD processors of same tier are comparable to each other provided they were released around same time. That is, Ryzen 5 and Core i5 CPU should perform similarly to each other if they both were released in the year 2023 around the same time.
It is also important to note that Core I is not the only tier from intel, they offer budget processors under Pentium and Celeron names, which fall below Core i3 in terms of performance.
Generation of the Chip
Right after the branding/tier part of a processor name, the first number which you see refers to the CPU generation. Since Intel long has been in a double-digit generation, we see the first two numerals to figure out the generation. In case a CPU is earlier than 10th generation then only the first numeral is seen.
A processor generation can be best understood as its age, the newer the generation of a processor the better it is in terms of performance and efficiency than the previous generations. Intel is currently on its 14th generation of processors.
Generally, a new generation of processor will be better than a similar processor from an older generation. There might even be a situation where you might find a Core i5 latest generation processor, outpacing a Core i7 processor which belonged to an older generation.
For example, Intel Core i5-14600K is far better than any, Core i7 ,9th or 10th or 11th generation processor in terms of both performance and power efficiency.
So, it’s not only important what tier you choose, you must also choose the correct generation of processor. Please don’t fall for the marketing traps where Core i5, i7 and i9 are used as marketing gimmick, when in reality it’s an older generation CPU with mediocre performance. CHECK YOUR GENERATION!
Performance Number/Model Number
The last three digits present in a processors name denote its performance number/model number (also referred to as SKU number). This number (made of up the last 3 digits), gives an indication towards the performance of a CPU in a given generation.
The higher the number, the better the processor is when compared to other processors of the same generation. For example, between Core i5-13400 and Core i5-13500 by looking at the last three digits you can easily and safely conclude that 13500 is the superior processor in terms of performance due to higher cores, clock speeds and cache.
Therefore, it’s important to compare different processors from a single generation through their performance number in order to identify the one which best suits your needs.
Performance Number/Model Number Suffix
Intel uses a letter as a suffix in the name of its processors in order to convey some important extra bit of information which helps customers to better compare between their various offerings.
It can be easily understood as, the letter at end of a processor name signifies its particular function/purpose.
Following is a list of all the letters used by Intel and their meanings:
- K: It means that the particular CPU is unlocked and can be overclocked to boost its performance.
- T: It indicated a processor with low power consumption.
- F: It means that the CPU does not contain an integrated graphics processor, and thus requires a discreate GPU in order to show display. (They are generally cheaper due this reason)
- KF: This is a combination of two letters, it means the processor is unlocked and can be overclocked and that it does not come with an integrated graphics processor.
- S: It means the processor is a special edition.
- G: It means that the particular CPU, contains an integrated graphics processor and thus does not need a discreate GPU to show display. The newer processors from Intel generally no longer contain the ‘G’ suffix instead now processors with these capabilities do not have any Suffix.
- X/XE: Highest performance, unlocked for overclocking
For laptops and mobile processors following letters are used:
- HX/HK: These are high performance processers and are overclockable. Therefore, they consume large amounts battery, leading to poor battery life but great performance.
- H: These are found in mid-range gaming laptops and offer great performance but are not unlocked thus not overclockable. They consume less energy than HK/HX processers.
- P: These processors are striking a good balance between performance and efficiency and are thus used in thin and light notebooks. They generally offer both good battery life and performance.
- U: These are used in budget laptops as they are power efficient processors giving good battery life, but they are poor in performance.
- Y: These are extremely low powered processors and give the best battery life for laptops but are very weak and only suitable for everyday tasks.
- G1-G7: For laptop and mobile processors Intel uses G1-G7 suffixes to indicate graphics level. The higher the number the better the graphics capability. For example: G6 graphics are better than G2 graphics.

